Recently when my satellite Internet connection slowed to a crawl, I assumed it had something to do with the satellite. I called Wildblue. The technician ran a check, informed me that the signal was weak, and advised me to check for snow or ice on the dish. The dish was clear, so the technician assumed the dish fell out of alignment for some reason. This was Friday. We scheduled a service call for Monday.
Over the weekend, I did some heavy-duty maintenance on my computer. I uninstalled programs I no longer use, deleted a bunch of files I no longer needed, and disabled some programs that were running in the background. Instantly, my Internet connection speed rose from about 200kbps to 950kbps – where it should be. I called and canceled the service call saving me fifty bucks.
The moral of the story – don’t assume a slow Internet connection is due to your ISP. It could be something as simple as an errant program running in the background.
First, test your connection speed. A couple good tools to test your Internet connection speed are CNet’s Broadband Speed Meter and Toast’s Internet Speed Test.
If your Internet connection is slower than it should be, here are some things to check:
- Router: If your modem plugs into a router which plugs into your computer, try bypassing the router by connecting the modem directly to one of your computers. If your connection is as fast as it should be, you just narrowed the problem down to the router.
- Background programs: Unbeknownst to you, your computer may be running programs on startup that consume system resources, including Internet bandwidth. Try disabling startup programs you don’t use or can’t recognize as performing any useful task. See “Disabling Background Programs in Windows,” later in this post for details.
- Firewall: A firewall designed to protect your computer from Internet intruders can gum up the works. Running too many firewalls can also be a problem. Check Windows Firewall (Start, Control Panel, Security Center). Check any Internet Security programs installed on your computer (such as Norton or McAfee), and check your router settings (if a router is installed). Try disabling all but one firewall – the router’s hardware firewall, if you’re using a router. One firewall should be sufficient.
- Domain Name Servers: The DNS matches the site address you type into your browser with the ID number of the computer on the Internet. Try changing your DNS, as I explain in a previous post, “Slow Internet? Try Changing Your Domain Name Server (DNS) Addresses.”
- Wireless signal interference: If you have a wireless router, a wireless phone or a neighbor’s wireless router may be interfering with the signal. Try changing channels, as I explain in “Weak Connection on Wireless Router? Try Changing Channels.
Disabling Background Programs in Windows
Windows features a configuration tool that enables you to disable programs when Windows starts. You can disable most of the programs to prevent them from running and then enable each program to identify the one that’s causing problems. To prevent programs from running in the background, take the following steps:
- Open the Start menu and click Run. The Run dialog box appears.
- Type msconfig and press Enter or click OK. The System Configuration Utility appears.
- Click the Services tab and click Hide All Microsoft Services to place a check in its box. By hiding Microsoft services you avoid accidentally disabling a service that’s critical for the operation of Windows.
- Click the Disable All button. This disables all services that are not critical for Windows to function properly.
- Click the Startup tab. A list of all the background programs that run on startup appears.
- Click the Disable All button. This removes the checkmark next to each program.
- Click OK. The System Configuration dialog box appears, prompting you to restart your computer.
- Exit any programs that are currently running and then click the Restart button. Windows restarts and then displays a dialog box indicating that you’re running Windows with a selective startup configuration for troubleshooting.
- Click OK. The System Configuration Utility appears.
- Click Cancel.
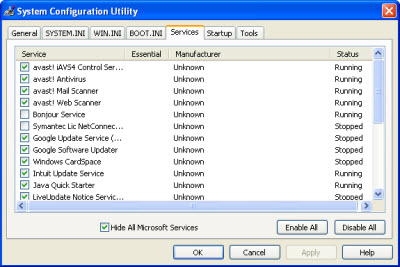
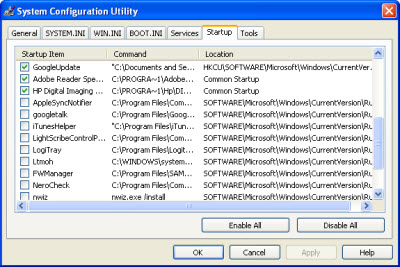
Test your Internet speed again. If it’s as fast as it should be, you know that one of the programs or services that you disabled was causing the problem. Use the System Configuration Utility to re-enable the programs and services one at a time (or two or three at a time), restarting Windows after each change. If enabling a program or service slows down your Internet connection, you’ve just identified the culprit.

hi
i have a difficulty trying to access the internet with four days.an error mesage keeps popping up which says that a programmerunning in the background maybe preventing the internet from working try again later? any idea what this problem might be.i have tried uninstall and install and full anti virus check and other and nothing wrong with these programmes.
Did you try disabling your background programs as explained in the blog post?